Damage & Risk#
Damage and risk assessments are critical for understanding the potential impacts of natural hazards on infrastructure systems. In this study, damage is estimated using hazard, exposure, and vulnerability data. We define risk as a function of these three key components:
This framework is applied to estimate the risks posed by natural hazards such as floods, earthquakes, tropical cyclones, and coastal flooding to infrastructure systems like roads and railways.
Estimation of Damage#
The conditional probability of failure of infrastructure assets when subject to an extreme hazard depends on their design and site-specific conditions. For global risk assessments, generic fragility curves are often used to estimate damage due to a lack of localized data. These curves relate the intensity of hazards to a damage probability based on infrastructure characteristics. For example, flood damage curves are often linear, relating flood depth to expected infrastructure damage (See Vulnerability Section).
The general approach is outlined in Figure 1. After processing the OSM data, we perform an exact overlay with the provided natural hazard data (a flood in Figure 1) Within our analysis, we identify each unique hazard intensity for each element. Following, knowing the affected area (in the case of a polygon element) or the length (in the case of a line element) of the affected asset, we use the pre-defined vulnerability curves to assess the damage for that asset for each unique hazard intensity. Finally, this can be summed to get a total damage per asset. If required, these damage values can be scaled according to Gross Domestic Products (GDP) or corrected based on available information design standards.
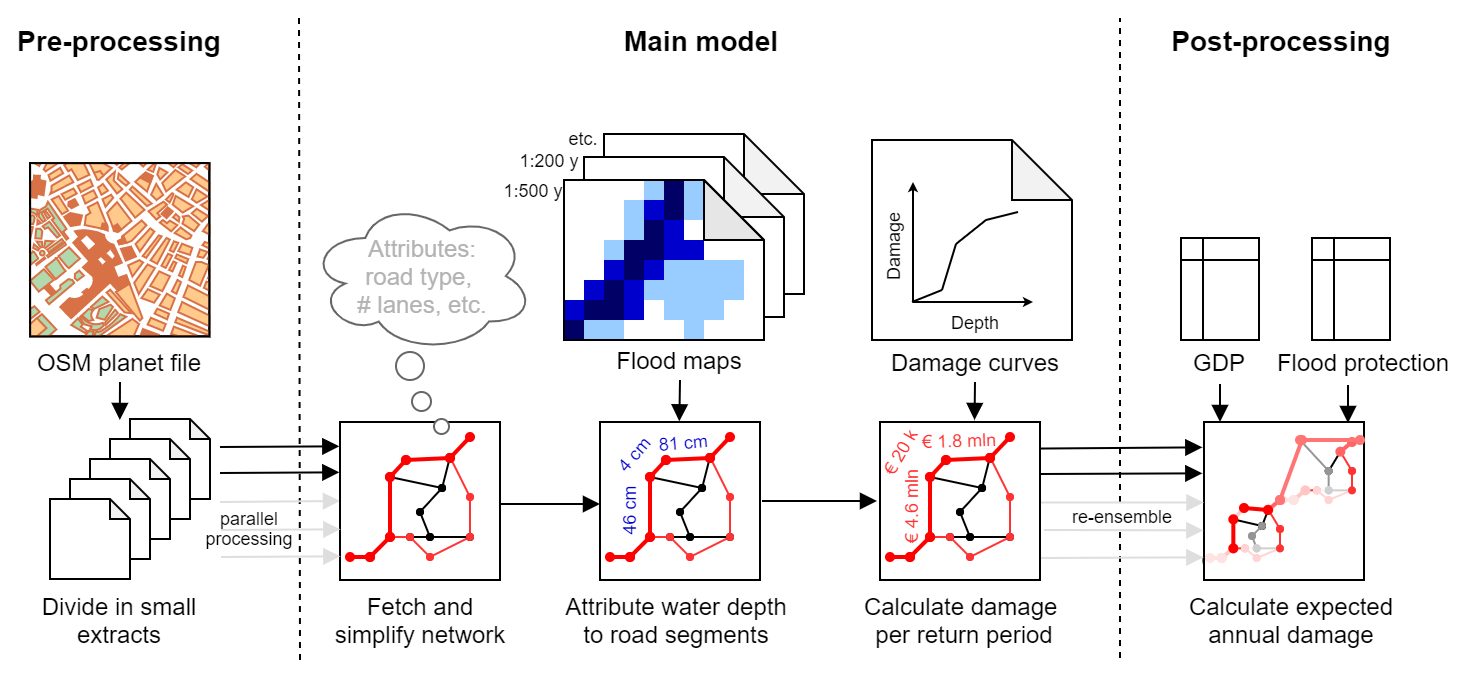 Figure 1: Damage assessment framework for critical infrastructure. Source: Van Ginkel et al., (2021).
Figure 1: Damage assessment framework for critical infrastructure. Source: Van Ginkel et al., (2021).
Estimation of Risk#
Risk estimation follows a trapezoidal approach, using exceedance probability loss curves to quantify risk. For each hazard, the probability of occurrence is multiplied by the expected damage to infrastructure, yielding the annual expected damage (EAD).
